|
Do you want to be a better CNC'er in 37 Seconds? Get Better Tool Life, Surface Finish, and Material Removal Rates Fast. It's that easy. You can install and get results now. |
| Quadrature to Rulon |
Quadrature refers to a specific scheme whereby an encoder
or linear scale can give both the amount and direction of movement. It accomplishes this by using two separate signals
generated from markings on the scale and observing the relationship of
the comings and goings of the markings relative to one another. The name derives because there is a 90 degree
phase difference between the two signals.
The quadrature technique also produces more resolution, when all
4 edges of the signal are used to determine the resolution.
The Quill is a spindle feature whereby just the spindle
cartridge may be raised and lowered using a rack and pinion without moving
the whole head. It is common on
manual milling machines and drill presses, but is usually omitted from
CNC milling machines.
Rack and Pinion is a type of mechanism for translating
rotation motion to linear motion. It
consists of a rack, which is a long toothed rod, and the pinion, which
is a round gear that engages the rack.
Rack and pinion drives are subject to a fair amount of backlash
unless carefully engineered, so they’re usually only found in applications
like plasma tables that don’t require the highest precision.
Where more precision is required, a leadscrew is generally employed.
See Also Leadscrew.
For a stepper motor, ramping is a technique of controlling
the acceleration or deceleration of the motor to ensure it arrives at
the desired speed when expected. If
you try to ramp the motor too quickly it can’t accelerate or decelerate
as fast as commanded and will be out of sync with expectations.
As a machining technique, ramping involves gradually
increasing engaging the tool until the desired final depth of cut while
moving along a path, either a straight line or sometimes a helical ramp. It results in less stress on the machine and
a better finish in the end of the day.
To move at the machine’s maximum rate of speed in order to reposition the cutter to a new location prior to beginning a new cut. Rapids can be many times faster than cutting speeds.
G-Codes support three common types of motion:
- Rapids (G0): Moving
the tool as quickly as possible, preferably without cutting (although
the machine usually doesn’t enforce this) in order to get to the next
location where cutting is desired.
- Linear Interpolation (G01): Linear interpolation is smoothly moving multiple
axes of the machine so the tool follows a straight line as closely as
possible. Since the line is usually
not aligned with an exis, this requires motion
from more than one axis to “stair step” together to produce this diagonal
motion.
- Circular Interpolation (G02/G03): Circular interpolation
is smoothly moving multiple axes of the machine so that the tool follows
a circular arc as closely as possible.
Since the axes only move in straight lines, a series of tiny lines
are used to simulate an arc. G02
causes the motion to be in a clockwise direction, while G03 is counter-clockwise.
A rectifier is a device that converts alternating current
(AC) to direct current (DC). It
is a component of a DC or Linear Power Supply such as may be used to provide
current for stepper or servo driver motors.

Recutting occurs when chips
are not evacuated quickly enough to avoid the cutting tool hit them again
after they’ve already been cut. This
forces the chip against the cut again, which is bad for surface finish
and tool wear.
One strategy to reduce recutting
is to use climb instead of conventional milling.
A regulated power supply is one in which a voltage regulator
circuit or component has been added to ensure voltage stays at a pre-determined
level as precisely as possible. Computers
and other logic circuits require regulated power supplies.
Motors do not.
Relative Coordinates, also called Incremental Coordinates,
refers to the system by which the part program determines how to move.
Absolute coordinates are expressed relative to a fixed position whereas
Relative Coordinates (see also) are relative to the current position of
the cutting tool. The G90 command
places the part program into absolute coordinate mode. G91 cancels absolute coordinate mode and places
the part program into relative coordinate mode.
Relative Zero is the name of the origin of the Relative Coordinate system, in other words, it is the current location of the tool. See Also Relative Coordinates.
A relay is an electronic (See Also Solid State Relay)
or electromechanical device that uses a small current to operate a switch. A type of very heavy duty relay used to control
large current flows (such as are needed for motors) is called a Contactor
(See Also Contactor). The control
signal for a relay is typically DC.
Repeatability for a CNC machine is the ability to reach
the same level of accuracy over and over again.
How accurately a CNC machine or component can discern
position. Encoders have a resolution
as do digital calipers and other devices.
Clearly, it is hard for accuracy (See Also Accuracy and Repeatability)
to exceed resolution. Typically
accuracy is much less than resolution, in fact.
Resolvers are rotary transformers
that produce a signal proportional to the rotor position. They are used on older machines before optical
encoders became readily available. Generally,
they only work with older controls systems and are often replaced with
optical encoders (See Also Encoder) when the machine is refitted with
a new control.
Resonance is a tendency to vibrate or oscillate at a
particular frequency. In stepper
motor systems, resonance can cause a phenomenon known as mid-band instability,
wherein resonance effects cause the system to lose synchronization. This basically means the motor is fighting the
driver, which is not delivering pulses in sync with the motor’s needs. The result is a loss of torque. Sophisticated drivers like Geckos are designed
to eliminate this problem.
A little knob at the top of a toolholder that the drawbar uses to hold onto the holder and pull it up into the taper (See Also Taper). The Retention Knob is gripped by a sort of collet-like arrangement on the end of the drawbar. It makes for much faster engagement than a threaded drawbar.
Retention Knobs are replaceable and typically have to
be replaced as the wear out.

Rhino 3D is a CAD program that may be used to generate
solid models.
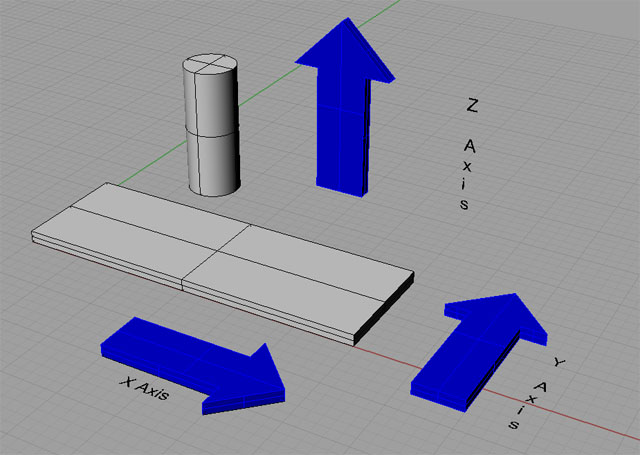
The right-hand rule is a convenient way to know the location of the X-, Y-, and Z- axes as well as which direction is positive. Simply hold out your right hand with the thumb, index finger, and second finger at right angles to one another. Point your thumb to the right (X-Axis), the index finger straight ahead (Y-Axis), and the second finger straight up (Z-Axis). Note that this only works for axes as defined for mills (See Also Axes):
Rigid tapping is a CNC capability where a tap is placed
in a tool holder and the machine spins the tap while lowering it at exactly
the correct speed to cut threads. It
is called rigid because an alternate method, called floating tapping,
allows the tap to float relative to the spindle so that the threading
process pulls the tap along at the right speed.
Rigid tapping requires precise synchronization of spindle speed
with Z-axis motion much like tapping on a lathe.
The ability of the machine to resist
deflection (See Also Deflection).
An imaginary plane parallel to the X and Y axes that represents a safe height at which the tool can move without hitting anything. Usually the R-Level is set to be 0.1” above the highest feature on the part.
Also called “Safe Z” in Mach 3.
Roughing means to machine a lot of
material without concern for surface finish.
A round column mill is similar to a drill press. It uses a round column to support the spindle.
Z-axis moves are made using a quill (see also Quill) because the
spindle cannot be moved along the column without losing x and y position.
This makes these mills less desireable
for CNC applications, because the entire machining operation must be completed
without moving the Z-axis except via quill, which has very limited travel.
A router table is a gantry style machine used with a
router. They’re usually designed
to cut wood or plastic, although they have some capacity for light aluminum
work as well.
Revolutions per minute, a common measure
of rotational speed.
RS232 is the Electronic Industry Association standard that defines a standard for how electronic devices can communicate serially. It is an older standard than the more modern USB (Universal Serial Bus) standard. See also USB.
RS274D is the Electronic Industry Association standard
that defines the G-Code CNC language used by nearly all CNC machines. This version was approved in February, 1980.
A
more recent definition by NIST is called RS274NGC, with the “NGC” standing
for “Next Generation Controller”. It
was developed by the
| Quadrature to Rulon |
|
Do you want to be a better CNC'er in 37 Seconds? Get Better Tool Life, Surface Finish, and Material Removal Rates Fast. It's that easy. You can install and get results now.
|
||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||