Tag That Photo User Guide - Part 5¶
Metadata Management and Technical Details¶
Understanding Metadata Management¶
What is Metadata?¶
Metadata is "data about data" - information embedded in or alongside your image files describing: - Who is in the photo (face tags) - When it was taken (date/time) - Where it was taken (GPS coordinates, location names) - What it contains (keywords, descriptions) - Technical details (camera settings, dimensions)
TTP's Metadata Philosophy¶
Tag That Photo is built on the principle that you should own your metadata. Your tags and organizational work should:
- Be portable - not locked in proprietary databases
- Use industry standards - readable by other applications
- Travel with your images - embedded in the files themselves
- Survive software changes - not dependent on any single vendor
This is why TTP writes metadata directly into your images using Adobe XMP format and other industry standards.
Metadata Standards Used by TTP¶
Storage Locations¶
For JPEG and TIFF Images¶
Metadata is embedded directly within the image file in multiple formats: - EXIF - Camera and technical data - IPTC - Descriptive information (keywords, captions) - XMP - Modern extensible format (includes face regions)
For PNG, RAW, and HEIC Images¶
Metadata is stored in an XMP sidecar file: - Same filename as image, with .xmp extension - Plain text XML format - Typically less than 20KB - Human-readable (open in any text editor)
Critical: When moving these images, always move the .xmp file with them!
Face Region Standards¶
TTP supports two face region metadata formats:
1. Microsoft Photo Region Info (MPRI)¶
- Used by Microsoft Photo Gallery
- Windows Explorer reads and displays these regions
- Good for Windows ecosystem compatibility
- Specification: Microsoft Photo 1.2 Schema
2. Metadata Working Group (MWG)¶
- Industry-wide standard
- Supported by Adobe, Apple, and others
- Broadest application compatibility
- Active standards organization
- Reference: MWG Guidelines PDF
Recommendation: Enable both formats in Settings for maximum compatibility.
How TTP Reads Metadata¶
When TTP scans an image, it reads from multiple locations and reconciles differences.
Title¶
Read from (in priority order): 1. XMP Dublin Core Title (/xmp/dc:title) 2. EXIF XPTitle (TagID 0x9C9B)
Logic: First non-empty value found is used; others ignored.
Description (Caption)¶
Read from (in priority order): 1. XMP Dublin Core Description (/xmp/dc:description) 2. IPTC Caption 3. EXIF XPSubject (TagID 0x9C9F)
Logic: First non-empty value found is used; others ignored.
GPS Location¶
Read from (in priority order): 1. EXIF GPS IFD location (/app1/ifd/Gps/subifd:*) 2. XMP EXIF GPS location (/xmp/exif:GPS*)
Logic: First non-empty value found is used; others ignored.
Address Information¶
Read from (in priority order): 1. IPTC XMP Extension for Address Of Location Created 2. IPTC Core nodes (Country, City, Region, RegionSubLocation)
Logic: First non-empty value found is used; others ignored.
Face Regions¶
Read from (both sources): 1. XMP Microsoft Photo Region Info (MPRI) 2. XMP MWG Region list
Logic: Regions synchronized; duplicates not imported.
Keywords¶
Read from (all sources, merged): 1. EXIF XP Keywords (Tag ID 0x9C9E) 2. EXIF XP_DIP_XML (Tag ID 0x4747) 3. IPTC Keywords 4. XMP dc:Subject list
Logic: All keyword lists parsed into individual keywords; duplicates reconciled and imported once.
Control Data¶
Metadata Date: XMP xmp:MetadataDate node parsed and stored to track when metadata was last modified.
How TTP Writes Metadata¶
When metadata writing is enabled, TTP writes to specific standard locations:
Metadata Write Locations¶
| Data Type | Write Location(s) |
|---|---|
| Face Regions (Name) | MWG:Regions/RegionList MS Photo:RegionInfo IPTC4XmpExt:PersonInImage |
| Face Regions (Location) | MWG:Regions/Area MS Photo:Rectangle |
| Keywords | IPTC Core:Keywords XMP dc:subject |
| Description | XMP dc:description |
| Title | XMP dc:title |
| GPS Coordinates | EXIF GPS IFD XMP exif:GPS* |
| Location (Address) | IPTC XMP Extension |
| Date Taken | EXIF DateTimeOriginal XMP Photoshop:DateCreated |
Metadata Writing Process¶
Writing happens as a background process: 1. You tag faces or add keywords in TTP 2. Changes saved to TTP database immediately 3. Background service queues image for metadata update 4. When system is idle, metadata written to image 5. XMP metadata date updated to track modification
Priority: User actions always have priority over background metadata writing.
Future-Proofing Your Tags¶
Why Standards Matter¶
By writing face tags using MWG and Microsoft standards, your tags: - Survive vendor changes - not locked to TTP - Work in other applications - see compatibility chart below - Remain accessible - XML text format, not binary - Follow industry direction - MWG widely adopted
Verifying Your Metadata¶
You can inspect metadata using free tools:
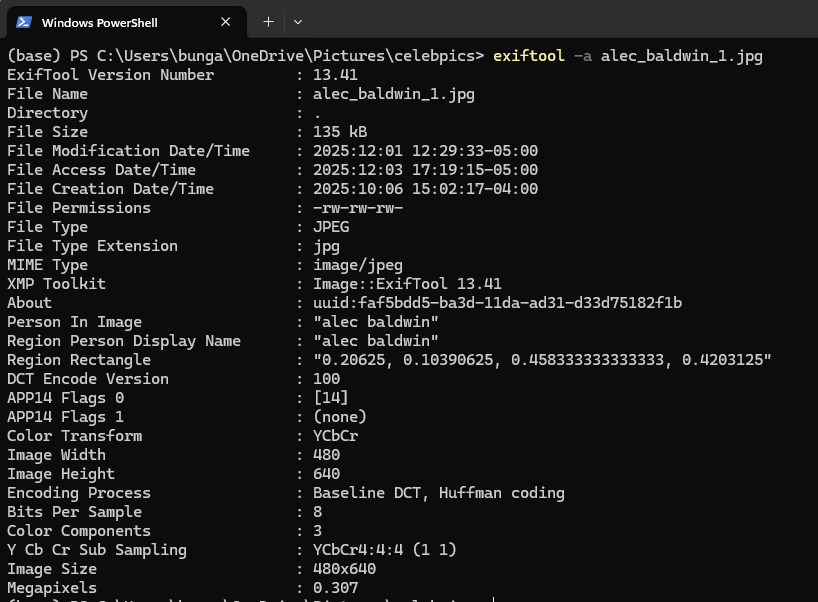
ExifTool (Command Line)¶
Free utility by Phil Harvey for reading/writing metadata.
Uses: - View all metadata in an image - Export metadata to CSV - Repair corrupted metadata - Batch metadata operations
Download: https://exiftool.org/
XnViewMP (Graphical Interface)¶
Free image viewer with excellent metadata display.
Features: - Visual metadata browser - Handles XMP sidecars - Can strip metadata if needed - Supports batch operations
Download: www.xnview.com
Cross-Application Compatibility¶
Applications That Read TTP Tags¶
| Application | Reads MWG/MS Face Tags | Reads Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Adobe Lightroom Classic | ✓ | ✓ |
| Adobe Bridge | ✓ | |
| Photo Mechanic 6 | ✓ | ✓ |
| ACDSee | ✓ | |
| XnViewMP | ✓ | ✓ |
| Photo Supreme | ✓ | ✓ |
| GIMP | ✓ | ✓ |
| Photoscape X | ✓ | |
| IrfanView | ✓ | |
| digiKam | ✓ | |
| Fast Picture Viewer | ✓ | |
| Zoner Photo Studio | ✓ | |
| Mylio | ✓ | ✓ |
| CyberLink PhotoDirector | ✓ | |
| Capture One Pro | ✓ | |
| Photos (macOS) | ✓ | |
| Preview (macOS) | ✓ |
End of Part 5: Metadata & Technical Details
Continue to Part 6: Troubleshooting & Appendix...